Evolution is a biological theory that postulates that all organisms on earth– plants, and animals have a common origin and their differences today are the result of modifications that occurred in successive generations. There is evidence of evolution that can prove this. Evolution claims that there has been a genetic variation that brings about the difference in the physical characteristics of different species.
Suggested Videos
Evidence of Evolution
We can broadly group the evidence of evolution into 5 broad categories:
- Relationship between organisms
- Anatomy and morphology
- Homologous Organs
- Analogous Organs
- Vestigial Organs
- Atavism
- Genetics
- Paleontology (study of fossils)
- Embryology
Let’s look at each of this evidence of evolution a little more in detail.
Relationship Between Organisms
The theory of evolution says that all organisms alive today have originated from a single ancestor. There are many similarities to prove these common origins:
- All organisms are made up of cells.
- The structure and functioning of individual organelles of cells remain the same in all organisms except with a few variations.
- Cells of the same kind and function form tissues in all organisms.
- All organisms grow, reproduce and multiply.
- All organisms are able to perform metabolism and generate energy to be able to live and thrive.
Anatomy and Morphology
Evolution also is proved by the similarities in the anatomy and morphology of different animals and plants due to the presence of:
Homologous organs

(Source: BiologyDiscussion)
These are organs that are similar embryologically but serve different functions in different organisms. This phenomenon is known as homology.
- Homology in plants: Thorns of a Bougainville are homologous to tendrils in creepers such as a money plant.
- Homology in animals: The structure of the heart in animals is an example of homology. The chambers in the heart are present in most animals -some have 2,3 and 4 chambers are seen in higher vertebrates. The forelimbs are present in all animals but modified to perform different functions- fins in aquatic animals, wings in birds, hands in humans etc.
Analogous Organs

These organs perform the same function in but develop from different structures in different species.
- Analogy in plants: In some plants leaves and in some their stems perform photosynthesis. Here, two differently originated structures perform the same function.
- Analogy in animals: Wings of an insect, bird and a bat(mammal) originate from different structures but all perform the same function of enabling the organism to fly.
Vestigial organs
These organs are non- functional and rudimentary in nature. However, they were very functional in the ancestors of the organism. This occurs due to the decreasing use of the organ which leads it to become small or non- functional in nature. Example of such a structure is the appendix and the wisdom teeth in human beings.
Atavism
This can be called as the reverse of vestigial organs where a structure or organ which has become extinct in the species has appeared in the future generations. Example of such a trait is the appearance of a short tail in human babies.
Genetics
The genetic code is made up of nitrogen bases. These base combinations are almost the same in all the organisms. Certain triplets of amino acid sequences also produce the same proteins in different organisms. This genetic code called the ‘universal genetic code’ remains identical to a large extent in most organisms proving the possibility of a common ancestry.
Paleontology

(Source: apologetics press)
The study of fossils is known as palaeontology. Fossils are formed when certain remains of organisms or plants get embedded in the soil or water and are preserved for many hundreds of years. They appear either as skeletal remains, footprints, moulds or intact structures as found in the snow. By studying fossils, we are able to establish similarities between the organism in the present to its ancestor in the past.
There can be many similarities that prove the common origins between different closely related animals and the differences can be studied to establish how they differ now and why. Fossils are very important evidence to prove the theory of evolution and common ancestry.
Embryology
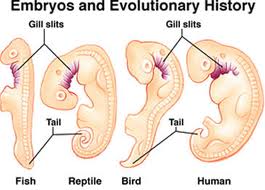
(Source: seanet.com)
It has been observed that the embryos of different organisms appear similar in early stages of embryo development. Some animals show structures present during embryonic life but which disappear in adult life or immediately before being born. And it is said by the ‘Recapitulation Theory’ or the’ Biogenetic Law’ by Von Baer that ‘Ontogeny repeats phylogeny’ which means that the embryo of an organism undergoes all the stages in the embryonic life as its evolutionary history. For example, a reptile embryo undergoes transformations from a fish-like appearance to amphibian-like features and then to a reptile embryo.
There are many theories that prove evolution is a fact and the truth of life on earth and this evidence of evolution only prove them more strongly.
Solved Example for You
Q: Who gave the Biogenetic Law?
- Charles Darwin
- Von Baer
- Hardy and Weinberg
- S.L.Miller
Sol: The correct answer is (b) Von Baer
Von Bar gave the Biogenetic Law or ‘Recapitulation Theory’ which says that ‘ontogeny repeats phylogeny’. Charles Darwin gave the Theory of Adaptive Radiation in Evolution. Hardy and Weinberg postulated the Hardy- Weinberg principle which gave an algebraic equation that helps determine the frequency of alleles in a locus or gene. S. L Miller gave the Miller’s theory that demonstrated how the first non- cellular life forms could have originated on earth by performing lab experiments.






For a biological update of human & ape evolution, please google “incridible mistakes PA 2019 Verhaegen”.
Human evolution