Did you ever wonder how various organisms reproduce? Not every organism is capable of reproducing sexually. There are so many hidden surprises for you in this chapter! We will study a different form of reproduction in organisms. It is known as asexual reproduction. We will have a brief look at its characteristics and types.
Suggested Videos
What is Asexual Reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction in which the new offspring arise from a single parent. The offsprings are identical to each other, both physically as well as genetically. They are the exact copies of their parent cell. Hence, they are ‘clones’. We observe asexual reproduction in both unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Features of Asexual Reproduction
- It involves a single parent
- There is no gamete formation or fertilization
- The whole process takes place in a small period of time
- Rapid multiplication and growth happens
- There is limited variation (genetically similar offsprings)
Modes of Asexual Reproduction
Organisms choose to reproduce asexually by different means. Some of the asexual methods are binary fission (e.g. Amoeba, bacteria), budding (e.g. Hydra), fragmentation (e.g. Planaria), spore formation (e.g. ferns) and vegetative propagation (e.g. Onion). Let us now look at the different modes of asexual reproduction in brief.
1) Fission
Fission means division. During asexual reproduction, the parent cell divides into two or more cells. Unicellular organisms show different patterns of cell division according to their cell structure. For example, an amoeba can divide itself into two at any plane but the division in euglena is longitudinal.
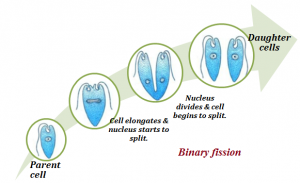
Fission can be of two types, namely, binary fission and multiple fission. In binary fission, parent cell divides into two equal halves called daughter cells. Daughter cells are identical to each other and to their parent cell. Organisms like the amoeba, bacteria, euglena, etc., exhibit binary fission.
During multiple fission, organism divides itself into numerous daughter cells. Examples of multiple fission are sporozoans and algae.
2) Fragmentation
Fragmentation is another mode of asexual reproduction. Multi-cellular organisms like planaria, spirogyra, etc. reproduce by fragmentation. The parent body divides into two or more fragments. Later, each fragment develops into a new individual.
3) Regeneration
When a lizard loses its tail, it grows a new one. This is known as regeneration. In many organisms, there are specialized cells, which can differentiate and grow into a new organism. Organisms like hydra and planaria also show regeneration. In these organisms, when the cell divides into numerous pieces, each piece proliferates and differentiates to regenerate new organisms.
4) Budding
Some organisms develop buds on their body. These buds develop into a new individual. This is known as budding. An example is a hydra. From the parent hydra, a bud arises which eventually matures into a new hydra. Once it gets mature, it detaches from the parent body.

(Source: brainly)
5) Vegetative Propagation
Plants reproduce asexually through their vegetative parts such as leaves, roots, stem, and buds. This is known as vegetative propagation. For example, onion bulbs, tubers of potato, runners/stolon, etc. Vegetative propagation is much faster than the sexual reproduction in plants. This can be done artificially as well, which is widely employed in horticulture.
You can download Reproduction in Animals Cheat Sheet by clicking on the download button below
Here’s a Solved Question for You
Q: Write a note on spore formation.
Ans: Spore formation is another means of asexual reproduction. Organisms which belong to the fungi group produce spores within a sac-like structure called sporangium. Under the favourable condition, sporangium burst to release spores which germinate to form new offspring.









n
freak
hi guys wanna scam
laddi song
hi sub to me parov stellar
hey i sub so wat now?
hi
i sub mr noob add me pls pls pls
add me too pls pls mr noob pls add me
yes lady gaga is here
want me to kill you mr noob……
i will be your little null hehe boi