The easiest thing to understand is that producers want good value for their products and consumers are willing to spend in accordance with the utility. So how do we satisfy both buyers and sellers? The answer is the equilibrium price. Let us take a look.
Equilibrium Price
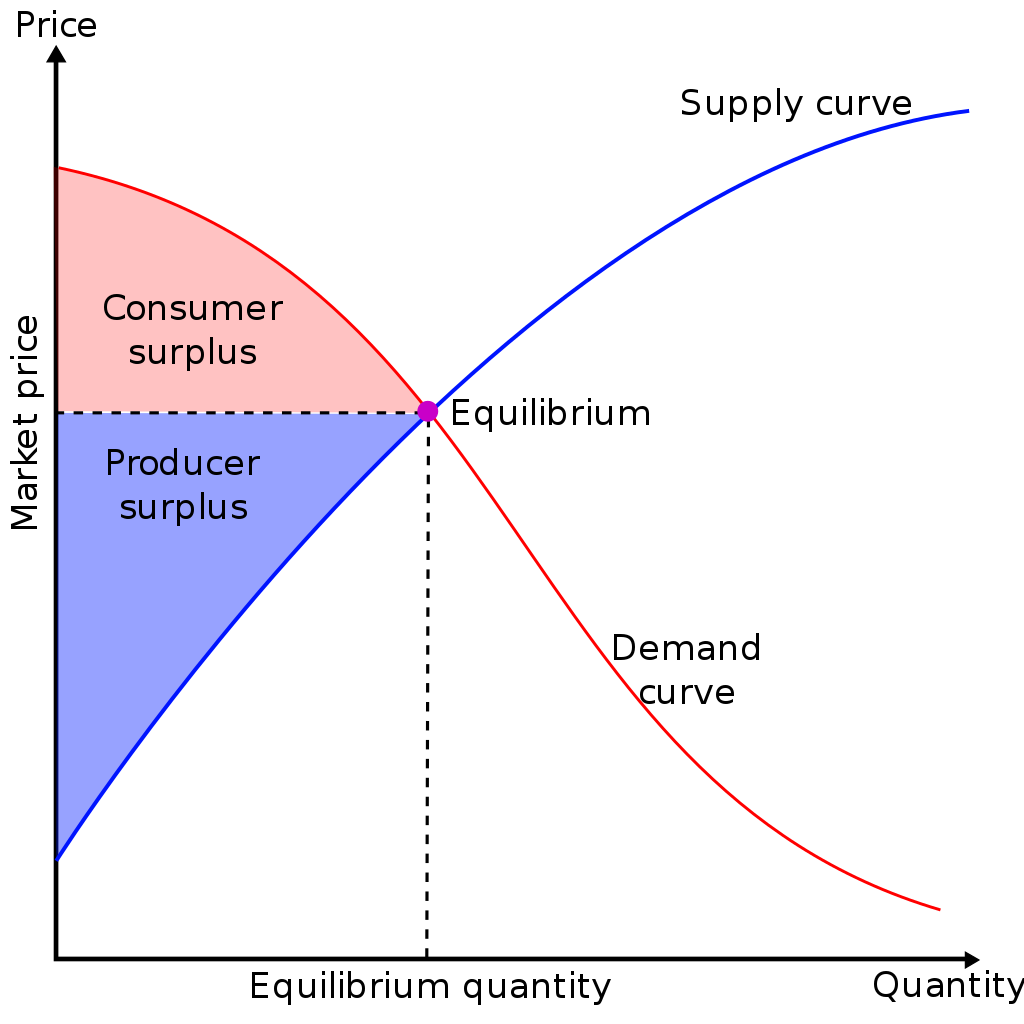
Equilibrium means a state of no change. Evidently, at the equilibrium price, both buyers and sellers are in a state of no change. Technically, at this price, the quantity demanded by the buyers is equal to the quantity supplied by the sellers. Both market forces of demand and supply operate in harmony at the equilibrium price.
Graphically, this is represented by the intersection of the demand and supply curve. Further, it is also known as the market clearing price. The determination of the market price is the central theme of microeconomics. That is why the microeconomic theory is also known as price theory.
Browse more Topics under Theory Of Supply
Supply and Demand Schedule
| Price | Quantity Demanded | Quantity Supplied | Impact on Price |
| 5 | 5 | 30 | Downwards |
| 4 | 12 | 25 | Downwards |
| 3 | 20 | 20 | Equilibrium |
| 2 | 25 | 15 | Upwards |
| 1 | 35 | 8 | Upwards |
A detailed look at the above supply and demand schedule reveals a bag full of information about the market. Most importantly, we can observe that the demand and supply become equal at a price of 3. Thus 3 is the equilibrium price.
Next, note how the impact on price is downwards when the price is too high for the buyer’s taste. Lastly, again the impact on price is upwards when it is too low for the supplier’s taste. To point out, the price tends to move towards the equilibrium mark.
Equilibrium Price Can Resist Change
As already mentioned, both consumers and sellers do not want to shift from the equilibrium price. In that case, the equilibrium price can change only when there is a change in both demand and supply. An increase in only demand or only supply is taken by horns by a self-adjusting mechanism.
When the price of commodity increases, the sellers flock to the market with their products for an opportunity to earn higher profits. This creates a condition of excess supply, ultimately leading to a surplus of the particular product in its market.
In order to sell this surplus, the sellers have to reduce the price. Effectively, the price continues to fall until it reaches the equilibrium level.
When the price of a commodity decreases, the consumers sense an opportunity to buy the product at a lower price. This creates gives birth to excess demand in the product’s market.
Consequentially, there starts brewing a situation of competition among the buyers which eventually pushes up the price. Eventually, the price continues to rise until it reaches the equilibrium level.
Note that the supply and demand schedule mentioned above is an indicator of all these processes.
Solved Example on Equilibrium Price
Q: How can we graphically represent the equilibrium?
Ans: The equality of quantity demanded and quantity supplied is an indicator of the established of the equilibrium. When we draw the demand and supply curves on a single diagram, the point of intersection of these two curves is the point of equilibrium. This is because at the point of intersection the demand and supply become equal to each other.






Supply is the
Group of answer choices
(a) limited resources that are available with the seller
(b) cost of producing a good
(c) entire relationship between the quantity supplied and the price of good
(d) willingness to produce a good if the technology to produce it becomes available.