Imagine a situation where a dictionary is created in Python that is used to store various attributes (keys) of a Book such as Title, Author, Pages, Edition, Publication, Year, etc. along with their distinct values. A user might want to fetch these values to check what type of data has been stored. That’s where the Python dictionary values() function comes in handy. This Python dictionary values() method is used to retrieve all the values associated with every key so we know what kind of information is stored.
Definition
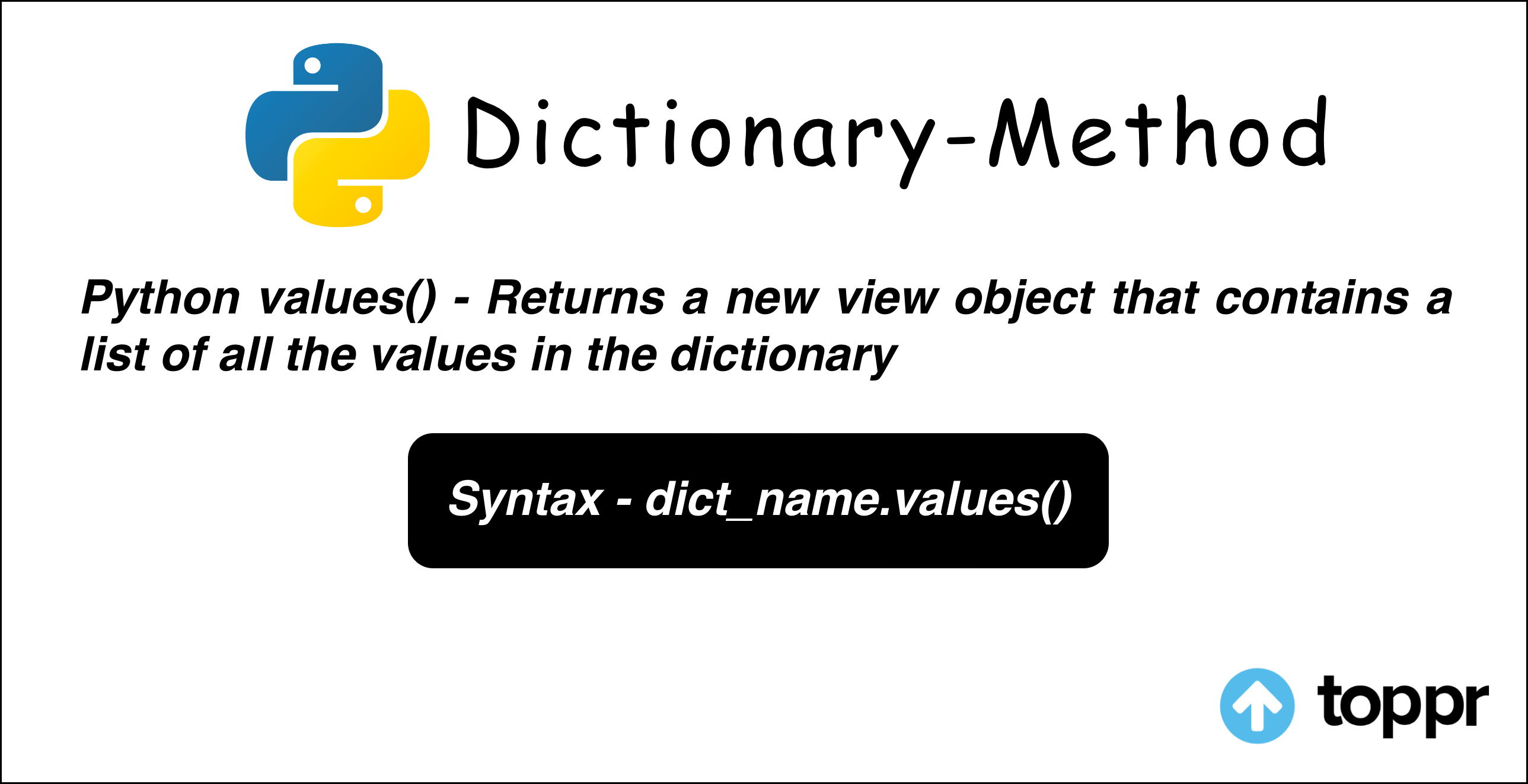
- Python dictionary values() function is used to return a new view object that contains a list of all the values associated with the keys in the dictionary.
- The Python dictionary values() method returns an object that only contains all the values in a dictionary.
values() Syntax
To use the Python dictionary values() function, we must follow the below syntax:
dict_name.values()
values() Parameters
The dictionary values() function does not accept any arguments or parameters.
Return value from values()
A view object is returned by the function which consists of a list of all the values in the dictionary. It is of type dict_values(). If the dictionary is changed, the view object will also reflect these changes and display the output accordingly.
Example 1: Get all values from the dictionary
Let us look at few examples to understand how Python dictionary values() function works.
Note – The order in which the values are displayed in the list might not always be the same.
Example
# Python program to illustrate values()
# creating a dictionary
stud = {'Name': 'Emily', 'Age': 28, 'Salary': 68000, 'City': 'Boston', 'Education': 'PG'}
val = stud.values()
print(val)
# another dictionary example
items = {'Fruit': 'Apple', 'Flower': 'Rose', 'Vegetable': 'Cabbage'}
print(items.values())
# empty dictionary
my_dict = {}
print(my_dict.values())
Output
dict_values(['Emily', 28, 68000, 'Boston', 'PG'])
dict_values(['Apple', 'Rose', 'Cabbage'])
dict_values([])
First, we created a Python dictionary named stud that contains the Students data. Then, using stud.values(), we get a list of all the values assigned to the keys in the dictionary. This list is then assigned to the Python variable val. The value of the val variable is then printed to the console.
Example 2: How values() work when dictionary is updated?
As we modify old values or add new key-value pairs to our dictionary, the values() method keeps track of them. In the below example, when the dictionary is updated, values are also updated to reflect the changes.
Example
# Python program to illustrate values()
data = {'Name': 'David', 'Age': 49}
print('Values Before updation:', data.values())
# adding new key-value pair to the dictionary
data.update({'Salary': 50000, 'Profession': 'Marketing Head'})
print('Values After updation:', data.values())
Output
Values Before updation: dict_values(['David', 49])
Values After updation: dict_values(['David', 49, 50000, 'Marketing Head'])
Example 3: Practical Applications of values()
The Python dictionary values() function can be used to access dictionary elements in the same way that we can access list elements; however, without the usage of values(), no other mechanism provides a way to access dictionary values as a list by index. This is illustrated in the following example.
Example
salary = {'Peter': 34000, 'John': 53000, 'Sally': 46000, 'Vanessa': 74000}
total = sum(salary.values())
print('Sum of all employees salary:', total)
for i in salary.values():
if i > 50000:
print('Salary > 50000 found, value is:', i)
Output
Sum of all employees salary: 207000
Salary > 50000 found, value is: 53000
Salary > 50000 found, value is: 74000
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How do you display a dictionary value in Python?
To fetch the values associated with the keys in a dictionary, Python dictionary values() method This method is used to retrieve all the values so we know what kind of information is stored.
The Python dictionary values() method returns an object that only contains all the values in a dictionary.
To use the Python dictionary values() function, we must follow the below syntax:
dict_name.values()
Example
num = {'I': 'One', 'II': 'Two', 'III': 'Three'}
val = num.values()
print('Values in Dictionary:', val)
num.update({'IV': 'Four', 'V': 'Five'})
print('Updated keys:', val)
Output
Values in Dictionary: dict_values(['One', 'Two', 'Three'])
Updated keys: dict_values(['One', 'Two', 'Three', 'Four', 'Five'])
Q2. How do you get a value from a dictionary in a list in Python?
After using the Python dictionary values() function, the Python interpreter returns a new view object of type dict_values(). To fetch every single value and display only that value, we take the help of the for loop.
Example
transport = {'2-wheeler': 'Bike', '3-wheeler': 'Rikshaw', '4-wheeler': 'Car', '6-wheeler': 'Truck'}
print('Values in dictionary are:')
for i in transport.values():
print(i)
Output
Values in dictionary are:
Bike
Rikshaw
Car
Truck
Q3. What are few restrictions to values in Python?
As compared to the Dictionary keys, Dictionary values, on the other hand, are unrestricted. There aren’t any at all. A dictionary value can be any type of object supported by Python, including mutable types such as lists and dictionaries, as well as user-defined objects. There are no restrictions on a single value appearing in a dictionary numerous times.






Leave a Reply