Obelia
Obelia refers to a genus of invertebrate marine animals which are available throughout the Earth’s oceans. It involves mainly marine and some freshwater animal species. Students can learn more information about obelia here.
Definition of Obelia
Obelia refers to the sedentary, marine colonial form which has an attachment on the surface of seaweeds, rocks, wooden piles, and molluscan shells in shallow water.
Moreover, this shallow water is up to 80 meters in depth. These are animals which belong to the class of Hydrozoa and Phylum Cnidaria and consist of various species.

Obelia begins as small, immobile animals which comprise of stalks and tentacles such that they resemble sea anemones. Moreover, these small animals are also known as hydroid polyps.
The common term for obelia happens to be sea fur. Also, a very unique aspect of this animal is that their reproduction strategy takes place two distinct stages. Furthermore, it takes two generations to complete.
Structure of Obelia
Obelia throughout its life cycle takes two forms: polyp and medusa. The first form is diploblastic, two true tissue layers – an epidermis (ectodermis).
In contrast, the second form is gastrodermis (endodermis), with a mesoglia which is jelly-like filling the area between the two tissue layers.
These animals carry a nerve net but have no brain or ganglia. Furthermore, the gastrovascular cavity is present where the beginning of digestion takes place. Afterwards, this cavity becomes intracellular.
These animals have incomplete digestive tracts. Moreover, digestion of the food takes place which enters and then this food is expelled through the same opening. The mouth is at the top of the body when the polyp stage takes place. Furthermore, this mouth is surrounded by tentacles.
The mouth is situated at the distal end of the main body structure when the medusa stage takes place. Furthermore, four gonads lie in the manubrium. Also, manubrium refers to the main body structure.
First of all, the food is enters through the mouth.
Then it certainly makes entry to the manubrium. The distribution of the food takes place through a canal system. Moreover, this canal system consists of four radial canals and an outer ring.
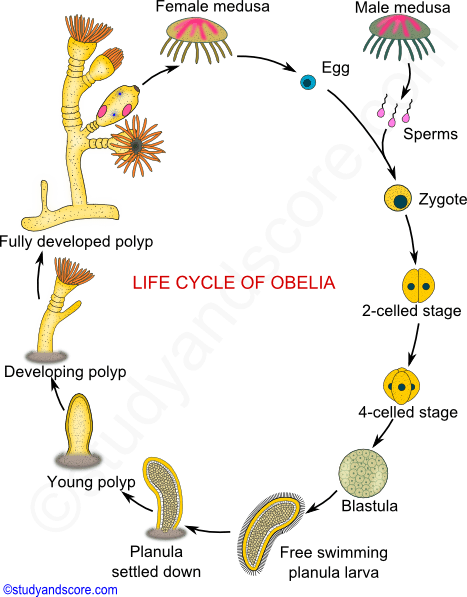
Life Cycle of Obelia
The polyp colony facilitates asexual reproduction. During this stage of life, the confinement of obelia is to the substrate surfaces.
There are gastrozooidsthis available on this mature colony. Furthermore, gastrozooidsthis refers to individual hydranths.
The gastrozooidsthis certainly expand and contract so as to facilitate the growth of this organism by feeding. The reproductive polyp gonozooids consist of medusa buds.
Other hydranths have a specialization for defence. Furthermore, the main stalky body of the colony comprises of coenosarc. Moreover, this coenosarc is covered by a protective perisarc.
The next generation of the life cycle begins when the release of medusae takes place from the gonozooids. This results in the production of free-swimming only male medusae velum.
Furthermore, these male medusa velum have gonads, a mouth, and tentacles. The physical appearance of the male and female medusae velum is probably indistinguishable.
Source- Studyandscore.com
The determination of the sex can take place only by the observation of the inside of the gonads. Most noteworthy, the inside of the gonads would certainly contain sperm or eggs.
The medusae certainly reproduce sexually and facilitate the release of sperm and eggs. The sperm and egg undergo fertilization to result in the formation of a zygote.
Moreover, the zygote certainly morphs into a blastula and consequently into a ciliated swimming larva. Also, this swimming larva is planula.
The planulae live free-swimming for some time but then they eventually attach themselves to a solid surface. Moreover, then the planulae start their reproductive phase of life.
When the attachment to a substrate takes place, a planula quickly changes into a feeding polyp. When the polyp keeps growing, it continues to develop the branches of other feeding individuals.
Finally, it results in the formation of a new generation of polyps by asexual budding.
Solved Question For You
Q1 Which of the following statement is not true when it comes to obelia?
A. These animals have complete and efficient digestive tracts
B. It refers to a genus of invertebrate marine animals which are available throughout the Earth’s oceans.
C. They begin as small, immobile animals which comprise of stalks and tentacles.
D. These animals are also known as hydroid polyps.
A1 The correct option is A., which is “these animals have complete and efficient digestive tracts.” This is because the correct statement is “these animals have incomplete digestive tracts.”






How is a Panda carnivorous ! Stupid site for stupid people….LMAO
Yeah, your tote right ’cause pandas eat bugs and bamboo so that makes it an omnivore. NOT a carnivore
THIS SITE IS SOOO PLAIN! And Not Smart(ANS)
no they are not lying over 1,200 giant pandas eat fish and fish is meat
hiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii people
this webite is so trash i hate it
to all mt blind lovers post something in sighn launguage
stop
this site isn’t lying over 1,200 giant panda’s eat fish
my homie left 6 comments on this site
Best site. Helped me a lot! Also, Billy is right. Over 1,200 pandas eat fish and they will eat other animals if it is an absolute must. So, “Panda Lover, If you really love pandas, you got to know more about them. Change your name too. People are gonna think you are a pre-school kid who just learned what pandas are. (You might be one, so..)
Also she said LMAO so, my 6 year old daughter says that while typing.