Cells come in various shapes and sizes. Based on the presence of a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, cells are broadly classified as Prokaryotic cells or Eukaryotic cells. Let’s learn about each in more detail.
Suggested Videos
Prokaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic cells lack both, a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound cell organelles. Examples of prokaryotes are blue-green algae, bacteria and mycoplasma.
Among prokaryotes, bacteria are the most common and multiply very fast. They are single-celled and range in size from 0.2 to 10 microns (about 10 times smaller than most plant and animal cells). Bacteria are found everywhere – in rocks, soil, ocean water. Did you know that there are approximately 10 times more bacterial cells than human cells in the human body? Now, most of these bacteria are found in the digestive system where they help in digesting food.
Browse more Topics under Cell The Unit Of Life
Based on the shape, there are four types of bacteria:
- Bacillus (rod-like)
- Coccus (spherical)
- Spirillum (Spiral)
- Vibrio (Comma-shaped)
You can download Cell: The Unit of Life Sheet by clicking on the download button below
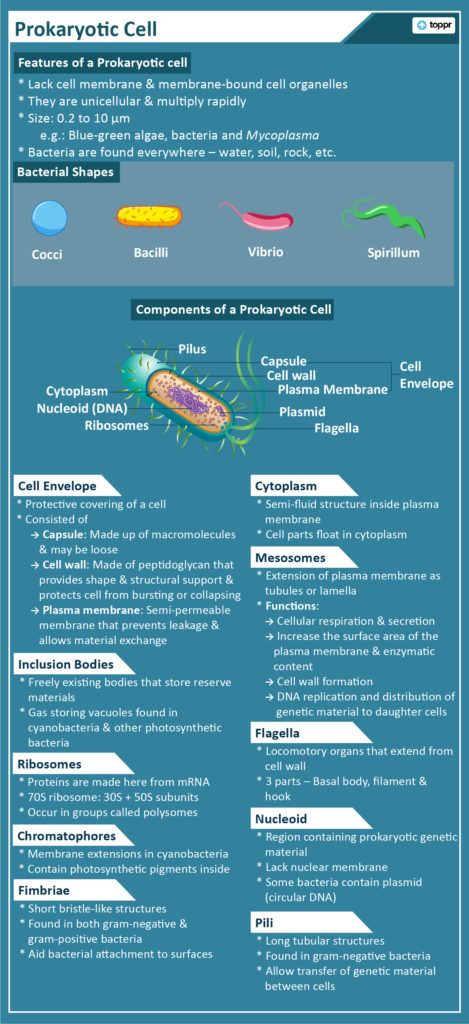
Components of a Prokaryotic Cell
A prokaryotic cell consists of different parts with special functions. Let’s look at each part in detail:

(Source: Wikipedia)
Cell Envelope
Cell envelope is the covering of a prokaryotic cell that protects it from injuries and shock. From outside to inside it has the following layers –
- Glycocalyx – It is made up of macromolecules and could be loose (called slime layer) or thick (called capsule).
- Cell wall – It is made of peptidoglycan and is just below the Glycocalyx. Its functions are to provide shape and structural support and protect bacteria from bursting or collapsing. So Bacteria can either take up Gram stain (Gram-positive bacteria) or cannot take up Gram stain (Gram-negative bacteria).
- Plasma membrane – This innermost layer is semi-permeable. It functions to prevent leakage from the cell and allow the exchange of material between the inside and outside of the cell.
Cytoplasm
It is the semi-fluid structure within the plasma membrane where the cell’s important parts float. Although prokaryotes lack membrane-bound organelles, they contain some other important structures described below.
Mesosomes
They are extensions of the plasma membrane into the cell in the form of tubules or lamella. They help with the following functions:
- Cellular respiration and secretion.
- Increase the surface area of the plasma membrane and enzymatic content.
- Cell wall formation.
- DNA replication and distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.
Chromatophores
These are also membrane extensions especially found in cyanobacteria. Chroma means colour. Therefore, these structures have photosynthetic pigments inside.
Ribosomes
In prokaryotes, the cytoplasm has small structures associated with the plasma membrane called ribosomes. Here, proteins are made from messenger RNA. Prokaryotes have the 70S ribosome which is made of 30S (smaller) and 50S (larger) subunits. Ribosomes generally occur in groups called polysomes.
Inclusion Bodies
They exist freely in the cytoplasm without a membrane. They act as storage for reserve material in prokaryotic cells. Special gas storing vacuoles are seen in cyanobacteria and other photosynthetic bacteria.
Flagella
Some bacteria have extensions coming from their cell wall called flagella that help them move. A single flagellum has three parts – basal body, hook and filament.
Pili and Fimbriae:
| Pili | Fimbriae |
| Long tubular structures | Short, bristle-like structures |
| Only in Gram-negative bacteria | In both, Gram-positive and negative bacteria |
| Help in transfer of genetic material between cells | Help bacteria attach to surfaces |
Nucleoid
Nucleoid is the genetic material in prokaryotes. It does not have a nuclear membrane. Many bacteria contain small circular DNA called plasmid.
Learn more about Eukaryotic Cell here.
Solved Example for You
Q: The intracellular compartments are not found in which of the following cells?
- Lower Plants
- Prokaryotes
- Higher Plants
- Eukaryotes
Sol: The correct answer is option “b”. Prokaryotic cells are the primitive unicellular organisms which have disorganized nucleus without a nuclear membrane.






Leave a Reply