We all know that plants can make their own food. Isn’t it an amazing thing? But did you know there are a few plants that cannot make their own nutrition? Let us have a detailed look at the incredible photosynthesis process and the factors that affect it.
Suggested Videos
Photosynthesis
Plants who can make their own food are known as autotrophs. But, there are few plants who cannot and are called as heterotrophs. The process by which plants make their own food is called as photosynthesis. The photosynthesis process occurs largely in the leaves of the plant which are known as the ‘kitchen of the plant’. In some cases, even the stems have the potential to perform photosynthesis.
Browse more Topics under Photosynthesis In Higher Plants
The Leaf

(Source: Sqizzes.com)
As mentioned earlier, the process of photosynthesis occurs in the leaf of a plant. The leaf is anatomically divided into many layers. Photosynthesis occurs in the mesophyll layer of the leaf, the middle layer, also known as palisade parenchyma. These mesophyll cells are abundant in special cell organelles called as chloroplasts which are responsible for photosynthesis.
Leaves also contain small openings on their undersurface known as ‘stomata’ which are responsible for gaseous exchange and are the source of CO2 that enters the leaf.
The Chloroplast
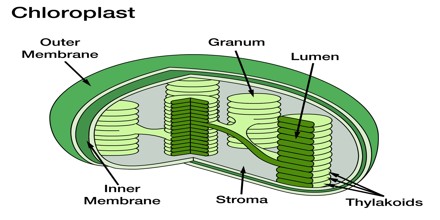
(Source: AssignmentPoint.com)
These are special organelles that inside which photosynthesis process takes place. Chloroplasts are double membraned organelles. The Chloroplast consists of disc-shaped thylakoids that are stacked together. Stacked thylakoids are called a ‘grana’. It is in the membrane of the thylakoid that pigment chlorophyll is present.
Photosynthesis Process

(http://photosynthesiseducation.com)
Photosynthesis process can be divided into two stages:
Light Reaction
This reaction is a light- dependent reaction and it is needed to produce energy molecules like ATP and NADPH. This reaction occurs in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast where the sunlight triggers of the reaction of chlorophyll pigment.
The excited chlorophyll releases an electron which is accepted by the H2 of water after its splitting. The reactions that happen are redox reactions and ultimately lead to the production of energy molecules- ATP and NADPH which are then needed for the subsequent synthesizing reactions that occur in the dark reaction.
Dark Reaction
This reaction does not literally occur in the dark but is named so because it is independent of light. This reaction can occur both in the presence and absence of light. Due to the scientists who worked to discover this cycle, this reaction is also called as the Calvin- Benson-Bassham cycle.
This reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast. This reaction uses the energy molecules generated in the light phase of photosynthesis and converts CO2 into glucose. The photosynthesis process can be summarised by the following equation:
6CO2+ 6H2O→C6H12O6+ 6O2 (in the presence of sunlight)
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis Process
There are few factors that promote or inhibit photosynthesis depending on their concentration :
- Light
- Temperature
- CO2
- Oxygen
Purpose of Photosynthesis
For the plants, photosynthesis helps generate glucose to be able to generate energy to perform other functions such as respiration, transport of water and minerals throughout the plant. Plants need energy to also perform other biological and biochemical processes to enable it to multiply. For other organisms, plants serve as food.
Solved Example for You
Q: Where does the light reaction occur?
- Stroma of the Chloroplast
- Thylakoid membrane
- Grana
- Both b and c
Sol. (d) Chlorophyll is present in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplasts. Stacked thylakoids are known as grana. So, both options b and c are correct.






How to remember the dark reaction in biology