Aldol Condensation, in organic chemistry, is a condensation reaction of enol aka enolate and carbonyl compound. When enol ions react with carbonyl compound it forms a β-hydroxyketone or β-hydroxyaldehyde. This process is followed by dehydration which results in conjugated enone. And Alpha-hydrogen atom is an atom in which the hydrogen atom is reacted with the alpha-carbon atom. Similarly, the beta-hydrogen atom is an atom in which the hydrogen atom is reacted with the beta-carbon atom. Let us learn about different reactions of the alpha-hydrogen atom.
Suggested Videos
What is Alpha-Hydrogen?
To understand alpha hydrogen we first need to understand alpha carbon. An alpha carbon is the first carbon that is joined to the functional group. In the case of aldehydes and ketones, a functional group is a carbonyl group. The functional group is responsible for the formation of alpha hydrogen.
Learn more about Carbonyl group here in detail.
The hydrogen present on the alpha-carbon is the alpha-hydrogen and it is slightly acidic in nature due to the carbonyl group and its resonance stabilization mechanism. Thus, alpha-hydrogen and its acidic nature are responsible for several different reactions which we will study in this topic.
Browse more Topics under Aldehydes Ketones And Carboxylic Acids
- Chemical Reactions and Uses of Carboxylic Acids
- Methods of Preparation of Carboxylic Acids
- Nomenclature and Structure of Carbonyl Group
- Nomenclature and Structure of Carboxyl Group
- Nucleophilic Addition Reaction
- Oxidation
- Physical properties of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Preparation of Aldehydes
- Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones
- Preparation of Ketones
- Reactions due to Alpha-Hydrogen
- Reduction
- Uses of Aldehydes and Ketones
Acidity of Alpha-Hydrogen Present in Aldehydes and Ketones
Due to the acidic property of α-hydrogen in aldehydes and ketones, the compounds undergo different types of reactions. The acidic property of α-hydrogen in aldehydes and ketones is because of the high electron-withdrawing capacity of the carbonyl group and resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.

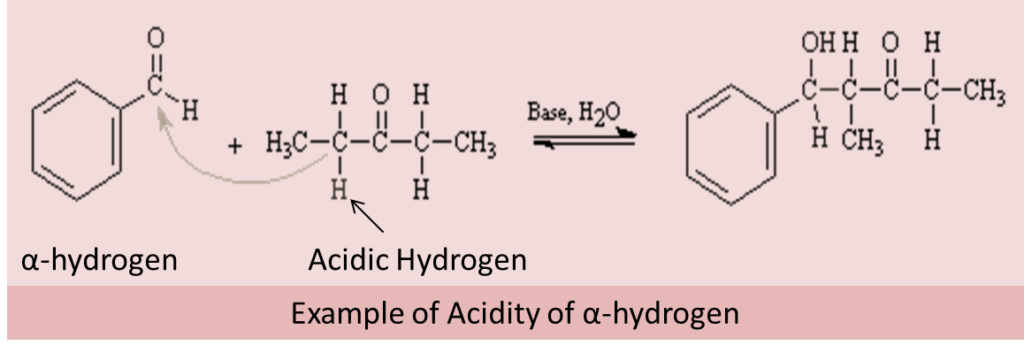
Aldol Condensation
Aldol reaction happens in aldehydes and ketones if the compounds contain no less than one α-hydrogen. Therefore, the reaction occurs in the presence of alkali (dilute). The dilute alkali acts as a catalyst in the reaction and helps in the formation of β-hydroxy aldehydes or aldol and β-hydroxy ketones or ketol.
This reaction is known as aldol condensation. The reaction derives its name from two different functional groups namely aldehyde and alcohol because these two products are present in the reaction. The β-hydroxy aldehydes or aldol and β-hydroxy ketones or ketol lose water molecules easily to produce α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
These compounds are aldol condensation products. The products due to ketones in this reaction are called ketol. However, the general name of the reaction is aldol condensation because they are fairly similar in their properties with aldehydes.

On mixing with dilute acid or base (aqueous), aldehydes containing α-hydrogen can react with themselves thereby resulting in the formation of β‐hydroxy aldehyde compounds or aldol compounds. This is because the resulting compound will have a functional group, aldehyde, and alcohol. Refer to the example below.

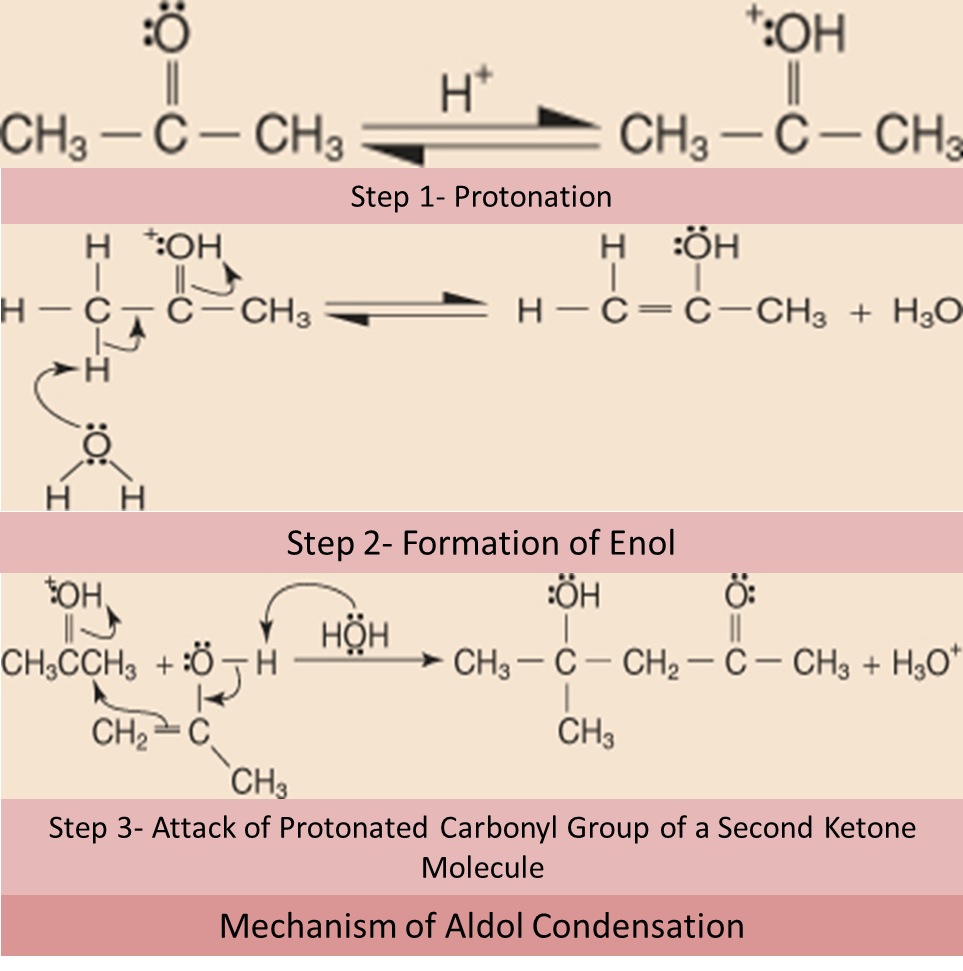
Mechanism of Aldol Condensation
The mechanism of aldol condensation initiates with the formation of carbanion intermediate. Refer to the steps below to observe the mechanism of aldol condensation in the presence of a base as a catalyst.
Aldol Condensation in Aldehydes with Base as a Catalyst
- Step 1: Removal of α-hydrogen from the base
- Step 2: The first step results in the formation of carbanion which undergoes a nucleophilic addition reaction with the carbonyl group present in the second molecule of the aldehyde (in this case ethanal). The second step results in the formation of the condensation product.
- Step 3: Protonation of alkoxide ion will occur due to reaction with water.
- Step 4: Heating of the aldol compound in the basic solution will help in dehydrating the product to form α β‐unsaturated aldehyde compound.

Mechanism of Aldol Condensation in Ketonic Compounds
The reactivity of ketones towards aldol condensation is less in comparison to aldehydes. However, a small quantity of aldol product formation is possible with the use of acid catalysts in the reaction. The aldol compound formed will soon dehydrate to form a resonance stabilized compound. Hence, the dehydration step of aldol condensation in ketonic compounds brings the reaction to completion.

Aldol condensation by acid catalysis includes two major steps. In the first step conversion of the ketonic compound to its corresponding enolic form will occur. In the second step, enol will attack the protonated carbonyl group.
- Step 1: Protonation of the oxygen of the carbonyl group occur.
- Step 2: The water molecule behaving as a base will remove the acidic α hydrogen leading to the formation of Enol.
- Step 3: The enol attacks a protonated carbonyl group of a second ketone molecule.
Cross Aldol Condensation Reaction
Cross aldol condensation refers to the aldol condensation reaction that occurs in between two different organic compounds, in this case, two different aldehydes and ketones. Therefore, the reaction leads to the formation of a series of product. If the α-hydrogen atoms are present in both aldehyde and ketone, the reaction will produce a mixture of four compounds.
The optimum result of cross aldol condensation reaction is possible if an aldehyde compound contains α-hydrogen and another aldehyde compound does not contain α-hydrogen. Refer to the example below to see the reaction with the mixture of ethanal and propanal.
Moreover, cross aldol condensation reaction is also possible if one of the components in the reaction mixture is a ketone.

Other Types of Reactions with α-Hydrogen
Cannizzaro Reaction
Aldehydes or ketones lacking α-hydrogen atoms can possibly undergo self-oxidation and reduction reactions on heating with alkali (concentrated). The reaction will result in the reduction of one aldehyde molecule to alcohol and at the same time oxidation of another aldehyde molecule to carboxylic acid salt.

Electrophilic Substitution Reaction
This reaction is possible in aromatic aldehydes and ketones at the ring in which the carbonyl group will behave as the meta-directing and deactivating group.

Halogenation of Ketones
Ketones having the α-hydrogen atom in the presence of a base react to form α-haloketones. For instance, methyl ketones and iodine reacts in the presence of a base to undergo complete halogenation reaction.

When sodium hydroxide reacts with iodine, it leads to the generation of sodium hypoiodite in solution. The reaction will result in the formation of sodium benzoate and iodoform. Additionally, the iodoform is a pale yellow color solid. Hence, this reaction refers to as iodoform test in order to detect methyl ketones. Refer to the example below.

Solved Examples for You
Question 1: Select the reaction which will not form a new carbon-carbon bond.
- Cannizzaro Reaction
- Wurth Reaction
- Aldol Condensation
- Friedel-Crafts Reaction
Solution: Option 1 (Cannizzaro Reaction).
Question 2: In which compound α-hydrogen extraction is possible by a strong base
- Amine
- Alkane
- Alkene
- Ketone
Solution Option 4 (Ketone).







Leave a Reply