Did you know the largest flower found on earth weighs fifteen pounds and can grow up to three feet! It is called the Rafflesia Arnoldii. And the smallest is the Wolffia and it is the size of a grain of rice. Flowers are more than pretty things, they are responsible for the reproduction of plants and are absolutely essential. Let us learn more about them.
Suggested Videos
Plants are majorly classified on basis of presence or absence of flower into flowering and non- flowering plants. A flower is a characteristic feature of flowering plants and is actually an extension of the shoot meant for reproduction. Flowers are attractive and appear in different colours and shapes to attract pollinators who help in pollen transfer.
Browse more Topics under Anatomy Of Flowering Plants
- Plant Tissues
- Tissue System
- Stem
- Leaf
- Inflorescence
- Secondary Growth
- The Fruit
- The Seed
- Classification of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Parts of a Flower

(Source: anmh.org)
Most flowers have four main parts: sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. The stamens are the male part whereas the carpels are the female part of the flower. Most flowers are hermaphrodite where they contain both male and female parts. Others may contain one of the two parts and may be male or female.
Before getting into parts, understand the classification of Flowers here.
- Peduncle: This is the stalk of the flower.
- Receptacle: It is that part of the flower to which the stalk is attached to. It is small and found at the centre of the base of the flower.
- Sepals: These are the small, leaf-like parts growing at the base of the petals. They form the outermost whorl of the flower. Collectively, sepals are known as the calyx. The main function of the calyx and its sepals is to protect the flower before it blossoms(in the bud stage).
- Petals: This layer lies just above the sepal layer. They are often bright in colour as their main function is to attract pollinators such as insects, butterflies etc to the flower. The petals are collectively known as the corolla.
- Stamens: These are the male parts of a flower. Many stamens are collectively known as the androecium. They are structurally divided into two parts:
- Filament: the part that is long and slender and attached the anther to the flower.
- Anthers: It is the head of the stamen and is responsible for producing the pollen which is transferred to the pistil or female parts of the same or another flower to bring about fertilization.

(Source: Wikipedia)
- Pistil: This forms the female parts of a flower. A collection of pistils is called the gynoecium.
Learn more about Inflorescence here.
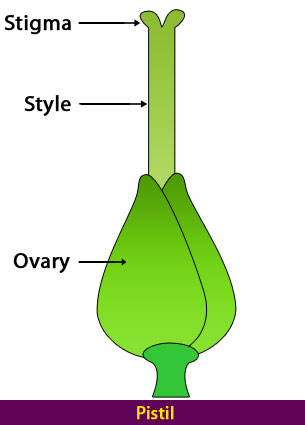
Pistil consists of four parts
(Source: Britannica)
- Style -is a long slender stalk that holds the stigma. Once the pollen reaches the stigma, the style starts to become hollow and forms a tube called the pollen tube which takes the pollen to the ovaries to enable fertilization.
- Stigma– This is found at the tip of the style. It forms the head of the pistil. The stigma contains a sticky substance whose job is to catch pollen grains from different pollinators or those dispersed through the wind. They are responsible to begin the process of fertilization.
- Ovary – They form the base of the pistil. The ovary holds the ovules.
- Ovules– These are the egg cells of a flower. They are contained in the ovary. In the event of a favorable pollination where a compatible pollen reaches the stigma and eventually reaches the ovary to fuse with the ovules, this fertilized product forms the fruit and the ovules become the seeds of the fruit.
Introduction to Leaf Structure
Solved Example for You
Q: What forms the androecium in a flower?
- Petals
- Stamens
- Sepals
- Pistil
Sol: The correct option is (b) Stamens
The androecium is the male part of the flower. A collection of stamens is an androecium.
FAQ’s for You
Q1. The flower is important to a plant because it helps in
A. Attracting
B. Production of Nectar
C. Pollination
D. All of above
Answer: All the flowers are important to plant as they attract pollinators by producing nectar, attracting pollinators and helps to plants in the reproduction process by pollination.
So, the correct option is ‘All of the above.’
Q2. Which of the following flower contain both stamens and pistils?
A. Perfect flower
B. Incomplete flower
C. Staminate flower
D. Bracteate flower
Answer: A bisexual flower is a flower that contains all the four whorls such as petals, sepals, the male reproductive structure (stamen) and female reproductive structure (pistil). Hence it is also called as a complete or perfect flower.
Q3. What are sessile and pedicellate flowers?
Answer: A flower which bears a stalk or pedicel is called as a pedicellate flower e.g. Hibiscus, Rose.
A flower which is borne directly on the stem is called to be a sessile flower. It is devoid of a stalk. Examples are sunflower florets, Sisyrinchium.
Q4. Flowers, which are pollinated by insects, are?
Answer: Insects such as butterflies, moths and bees visit flowers for nectar. These flowers have to be large, colored, showy and scented so that they can be easily spotted by insects. While feeding on nectar the pollens attach onto their body. When the same insect visits another flower it transfers the pollen to the stigma of that flower leading to pollination.








Use the
competitive examination
The apps is very helpful, but in the registration there is no Nigeria phone code?
seems like a good app,but,there countries missing,there is no ZAMBIA There,alot of african countrys not there for registraction,…what do we do for like us to register whose country is not there