India is a geographically rich and diverse country. Our country has all the features that one expects from a country. It has deserts, coastal areas, mountains, and plateaus. So yes, these are the physical geography features of our country. Here let’s take a look at the physical map of India and the other primary physical geography of India.
Suggested Videos
Indian Physical Geography
Based on physical features, India physical geography is broadly divided into the following sections-
- The great mountain of North
- Northern Plain
- Peninsular Plateau
- Coastal Plains
- Thar Desert
- Islands
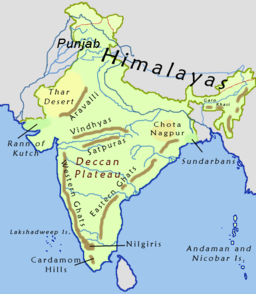
[Source: Wikipedia]
The Great Mountain of North
The key mountain of the North is the Himalaya. Spread over 2400KM, it covers Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh. The Himalaya comprises of three parallel ranges in its longitudinal extent. These include Himadri or Inner Himalaya or Greater Himalaya, Himachal or lesser Himalaya and Siwaliks or Outer Himalaya.
- Himadri: It is the Northernmost range. The average height of this range is 6000 Metre. The average width of this range is 120 KM. It comprises of most of the highest peaks such as – Mount Everest, Nanga Parbat, Kanchenjunga. Also, Ganga and Yamuna is originated from this range
- Himachal: It lies between the Himadri and Siwalik range. The average height of this range is 4000 Metre. The average width of this range is 60-80 KM. Important ranges in this are – Dhaula Dhar, Pir Panjal, Mahabharata. Famous hill stations such as Shimla, Mussoorie, Nainital etc, are located in this range
- Siwaliks: It is the outermost range. The average height of this range is as much as 1000 Metre. The average width of this range is almost 10-50 KM. Valleys which lies between the Himachal and Siwalik are called Duns
Browse more Topics under Introduction To Indian Geography
Northern Plain
Northern plain lies between the great northern mountain and peninsular plateau. It is formed by the three major rivers – Ganges, Indus, Brahmaputra and their tributary rivers. This plain covers the area of Indian states Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana, West Bengal, Assam. The plain is very fertile as it is formed by deposition of rivers. It is the source of major food grains in India. Northern Plain is divided into three sections- Punjab Plains, Ganges Plains, and Brahmaputra Plains.
- Punjab Plains: It is formed by the river Indus and its five tributaries – Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Sutlej, and Beas. Punjab and Haryana come under this plain. A larger part of this plain is in Pakistan.
- Ganges Plains: The plain is formed by the river Ganges and its tributaries. Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Bihar, Haryana, and West Bengal lies in this plain. It is the largest part of the Great Indian Plain.
- Brahmaputra Plains: It is built by the Brahmaputra and its tributaries. The plain is known as Assam Plain as most of its part is in Assam.
Division on the basis of Physical Features
Northern Plain is also divided based on the physical geography features. From North to South it is divided into – Bhabar Region, Terai Region, Bangar Region, Kadar Region.
- Bhabar Region: It lies in the foothills of Himalaya and is almost 8-16 km wide. The region mostly contains stones and pebbles. Here the flow of the rivers is fast.
- Terai: Terai lies south of Bhabar and is 15-30 km wide. It is covered by thick forest and the area is good for cultivation. Here, the river speed is fast.
- Bangar Region: It lies south of Terai and is less fertile in nature.
- Kadar Region: Kadar lies south of Bangar and is fertile land that is prone to floods.
Peninsular Plateau
Peninsular Plateau lies south of northern plain. The shape of this plateau is similar to a triangle whose base lies on the southern edge of the northern plain and Kanyakumari is the apex. Its average height is as much as 600-900 Metre. The Anamudi (2695 Metre) of Kerala is the highest peak of peninsular India.
Rounded hills and shallow valleys are found in this region. Formed from the Gondwana land, it is one of the oldest lands of the earth. Peninsular Plateau can be divided into two sections
- Central Highland: It is situated to the north of Narmada river. The plateau consists of Malwa Plateau, Chotanagpur Plateau, Meghalaya Plateau, Vidhya Range, Satpura Range, and the Aravali Range. The highest peak here is Guru Shikhar (1722 M).
- Deccan Plateau: It is bounded by the Satpura Range in the north, the Eastern Ghats in the east and the Western Ghats in the west. Rivers of Deccan Plateau (Kaveri, Godavari, Krishna) flows from West to East. Deccan Plateau consists of Andhra Plateau, Karnataka Plateau, and Maharashtra Plateau.
Thar Desert
The only desert of India is the Thar Desert. A major part of this desert lies in Rajasthan but a portion of it is spread in Gujarat, Haryana, Punjab, and Pakistan. Luni is the only river which flows from this land. The desert receives only 150mm rainfall in a year. It is also known as the Great Indian Desert or Marusthali. Also, the Great Rann of Kuchchh falls into this desert.
How is the Climate of Ladakh Dessert – Cold or Hot? and Which is the Hottest Dessert in the World?
The Coastal Plains
Coastal plains are situated along the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea. It is divided into – Eastern Coastal plain and Western Coastal Plain.
- Eastern Coastal Plain: It lies along the Bay of Bengal and is 1100 KM long. The plain covers West Bengal, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu. Here, the main rivers are Mahanadi, Godavari, Kaveri, and Krishna.
- Western Coastal Plain: It lies along the Arabian sea and is 1400 Km long. The plain covers Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, and Kerala. Main rivers here are Tapi, Narmada, and Mandavi.
Islands
India has two groups of islands:
- Andaman and Nicobar: It is located in the Bay of Bengal and lies 1255 Km of south from Kolkata. The groups of islands are divided into Andaman islands in the North and Nicobar Islands in the South.
- Lakshadweep: Lakshadweep lies in the Arabian Sea and is about 200-300 Km from the coast of Kerala. It consists of 36 islands.
Solved Examples for You
Question: Name the two volcanoes in Andaman and Nicobar?
Answer: Barren Island and Narcondam are the two volcanoes in Andaman and Nicobar







Border of Bangladesh with India. W.bangal. meghalay. Asaam.Tripura and Mijoram. Please correct your post.
Very nicely explained ” different climate of India”
Thanks for sharing such a answers
I liked it
Indian political geography has not been updated. There are 28 states and 8 union territories. Please keep up-to-date