A collection of chemical reactions that takes place in the body’s cells that convert the food we eat into the energy needed to power everything we do, from moving to thinking to growing is called as metabolism. It is the basis of living as without metabolism, our body will not be able to function. Let’s find out more.
Suggested Videos:
What phases does metabolism involve?
The process of metabolism occurs in two phases namely anabolism and catabolism.
Anabolism
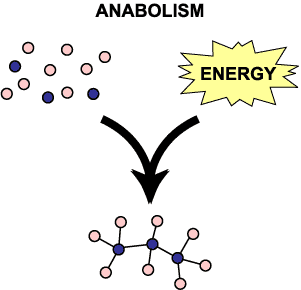
Involves reactions that build up complex molecules from simpler ones.
Monosaccharides form polysaccharides by glycosidic bonds, amino acids form proteins by peptide linkages, nucleotides form nucleic acids by phosphodiester bonds.Anabolic reactions commonly are condensation reactions where water is the by-product of the reaction.The purpose of an anabolic reaction is to form complex compounds. It absorbs energy in this process and so is an endergonic process. It is the process of anabolism that creates new cells, muscles, and other tissues.
Example of an anabolic process: Gluconeogenesis
Browse more Topics under Biomolecules
Catabolism
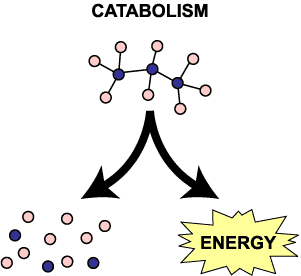
Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules. This occurs by the process of hydrolysis where macromolecules are broken down into their respective monomeric units. Hydrolysis reactions require the consumption of water molecules to break the bonds within the polymer. Unlike an anabolic reaction, catabolism is exothermic where heat is released.
Example of a catabolic process: Glycolysis.
It is important to note that both anabolic and catabolic processes do not occur in isolation and are always linked with one another.
Important metabolic processes:
- Digestion: This metabolic process begins with the ingestion of food from the mouth. It travels through the oesophagus to the stomach, the small intestine and the large intestine. From the time it is ingested, the food is subjected to various physical and chemical substances. The chemical substances that are released by different cells of the body are called enzymes. Enzymes are responsible for facilitating a metabolic reaction. Different enzymes from different glands in the digestive tract act on the food and eventually break it down into amino acids, fats, fatty acids and simple sugars all of which are needed to provide the body with energy and nutrients.
- Circulation: Once the food is broken down into simple absorbable monomeric units, these are transported into the blood to be circulated to other parts of the body for storage in the muscles, liver or as fat in adipose tissues.
- Excretion: this is the process where the waste products of metabolic reactions are eliminated from the body through urination, defecation, sweating, and breathing. The waste substances are produced as a result of the catabolic reactions. The organs that help in excretion are kidneys, intestines, skin, and lungs.
- Regulation of body heat: Apart from these three processes, the body performs one more important function- regulating the body temperature. The energy that is released after a catabolic reaction is accompanied by heat. This heat generated is responsible for keeping a steady body temperature at all times. The body has the potential to vary temperatures at different times based on the body’s physiological and the environmental conditions.
Solved Example for You
Q: Which of the metabolic process breaks down complex substances into simpler ones?
a. Anabolism
b. Catabolism
c. Both a and b
d. neither of the above
Sol: b. Catabolism
Catabolism is a metabolic pathway that breaks down complex substances to simpler ones accompanied by the release of heat with water as a by-product.







DNA consists of thymine or thiamine??