There are many uses of tense. In English grammar, we use present tense to talk about something that is going on now(currently) or that is true now and at any time. In other words, we use present tense to describe an event in real-time, i.e. happening at that very moment. Let us learn more about the present tense and its types.
Types of Present Tense
The present tense is of four types. Namely,
- Simple present tense
- Present continuous tense
- Present perfect tense
- Present perfect continuous tense
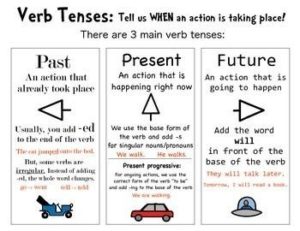
(Source: pineterst)
Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense uses the same verb form as the root form of the verb. We use the simple present tense in the following conditions:
- To show a fact or something that is always true
- For activities that we do daily -regularly or habitually
- To express thoughts, feelings, opinions and beliefs
- For a planned action or an event that will happen in the future
- We use this tense with a few adverbs to indicate something that happens rarely
- We use it in news, reported speech such as in sports commentaries, a narration of books and stories etc
- For schedules, plans and programmes
- To give instructions
Learn more about Past Tense here in detail.
Formulating a Simple Present Tense
When the singular form of the subject or a singular pronoun is used, the verb is used in the simple present tense by adding a ‘-s’ to it. For example,
- This person goes to the library often.
- When does the flight to Seychelles depart from Mumbai airport?
- I always wake up at 6 am.
- We agree with most of your plan.
- I like chocolates.
Browse more Topics under Tenses
- Introduction to Tenses
- Present Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Continous Tense
- Past Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Continous Tense
- Past Perfect Continous Tense
- Future Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Continous Tense
- Future Perfect Continous Tense
- Sequence of Tenses
- Uses of Tenses
Present Continuous Tense
This tense describes a continued or ongoing action at the present time. In other words, it expresses an action which is in progress at the time of speaking and has not yet been completed. In the following conditions we use the present continuous tense:
- As mentioned above, when an action that is occurring at the time of speaking
- When an action in the future is mentioned without specifying when it will occur
- When we talk about a planned or arranged event or action that is set to take place at a specified time in the future.
- In conditions where the action or event is occurring but not necessarily while we speak
- It is used in a changing situation
- We use it with adverbs such as ‘always’ which describe an action that happens frequently.
Formulating the Present Continuous Tense
It is formed from the present tense of the auxiliary verb ‘to be’ and the present participle of the verb ‘-ing’. For example,
- The noise is beginning to give me a headache.
- I am complaining to his mother about him.
- Why aren’t you doing your homework, Ravi?
Learn more about Future Tense here in detail.
Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense is used in case of repeated actions, in those actions where the time is not important, and actions that began in the past but are not finished yet and will probably finish in the present as we speak. We can use the present perfect tense in the following scenarios:
- For actions or events that began in the past and have continued into the present
- To show an action that has been completed
- To indicate a time period that has not yet finished
- Used with phrases that begin with “This is the first” or “second time” and so on.
- To describe or express an action that is repeated in the past
- Used to indicate or describe actions that have been completed in the recent past
Formulating the Present Perfect Tense
To form the present perfect tense, we need to use the simple present tense of the auxiliary verb ‘have’ or ‘has’ based on whether the noun being referred to is plural or singular. The past participle of the verb follows the auxiliary verb. We can also write as: have/has + past participle. Let us see some examples,
- We have known each other for a very long time.
- There have been many contenders for this role.
- Has there ever been a war during your lifetime?
- I have just eaten.
- We have had the same car for 8 years.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
To describe or indicate an event that is going on at this moment we use the present perfect continuous tense. We use this tense in the following conditions:
- To describe an event that began in the past and is continuing into the future
- To tell about an activity or event that began in the past and is now over(just recently completed or over)
- When there is no mention of time.
Learn more about Uses of Tenses here in detail with examples.
Formulating the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The two parts of the present perfect continuous tense are:
- The present perfect tense of the verb ‘to be’: ‘have been’ or ‘has been’ and
- The present participle of the main verb ‘-ing.
Some examples of present perfect continuous tense are,
- My hands are very dirty as I have been painting the walls.
- They have been trying to contact her.
- I have been working for them for the last seven months.
- The party has been going on all night.
Solved Example for You
Q: We ________in Chennai for six months.
(a) Had been living (b) Living
(c) Have been living (d) Are living
Sol. (c) have been living. Since the sentence talks about only one event, option (a) had been living is incorrect as it is used in past perfect continuous scenarios. Option (b) and (d) are both incorrect as they are not present perfect continuous as the sentence is. Option (c) is the correct answer as it is present perfect continuous tense.








What is the present perfect form of “He does not smoke”?
What is the difference between “He does not have to smoke” and “He has not smoked”?
Hello