You have heard your mother scream at you for being in the swimming pool for long as the ‘chlorine’ water could darken your skin. Right? Is it that bad? Life wouldn’t exist if it weren’t for the chlorine compounds. In this chapter, we will look at this element, its compounds and its uses.
Suggested Videos
Chlorine
Scheele manufactured a gas in 1774 by the activity of hydrochloric acid on manganese dioxide. In 1810, Davy built up its elementary nature and recommended the name Chlorine by virtue of its colour. It is greenish-yellow and it has a pungent smell.

Preparation Methods
1) We can prepare the gas by heating manganese dioxide along with concentrated hydrochloric acid. We can also prepare the gas by the activity of hydrochloric acid on bleaching powder (or) lead dioxide potassium (or) permanganate.
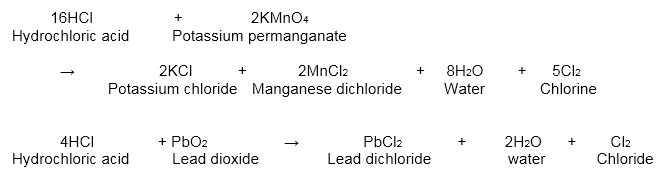
2) Electrolytic Process
We can acquire the gas by the electrolysis of salt water in a Nelson cell. This is the least expensive technique and gives the purest form of the gas.
3) Deacon’s Process
In this procedure, we can manufacture the gas by the oxidation of hydrochloric acid in the presence of cuprous chloride at 723K and a pressure of 1 atmosphere.
Physical Properties
- Chlorine is a greenish-yellow gas. It has a pungent odour.
- It has a boiling point of 239.11K and a melting point of 171.6K.
- The gas is harmful to nature.
- It is 2-5 times denser than air.
- It can be effectively condensed.
- The gas is marginally dissolvable in water.
- Its valency is 7.
Chemical Properties
- It breaks up in water to give a firmly smelling, yellow arrangement- chlorine water. It loses its yellow colour when it remains in the daylight. This is because of the arrangement of a blend of hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid.
- Hypochlorous acid, being unsteady, breaks down and releases nascent oxygen. The oxygen so shaped is in charge of the bleaching and oxidizing properties of chlorine.
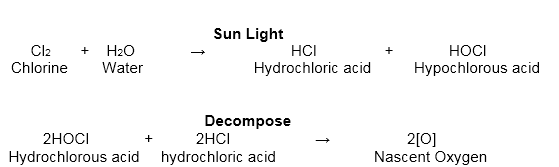
- It joins particularly with all non-metals except nitrogen, carbon, and oxygen. It reacts very fast with most of the metals. This reaction results in the formation of chlorides.
- It has an extraordinary liking for hydrogen. It reacts with hydrogen in the presence of light with a blast to form hydrochloric acid.
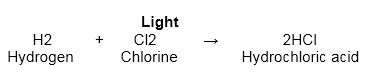
- Chorine breaks down a few hydrogen compounds to shape hydrochloric acid.
- It is a decent oxidizing agent; it oxidizes ferrous to ferric, sulfur dioxide to sulphuric acid, sulfites to sulfates, and iodine to iodic acid.
- Moist chlorine, because of the release of nascent oxygen, goes about as a very powerful bleaching agent. It fades organic matter or vegetables.
- With slaked lime, it frames bleaching powder.
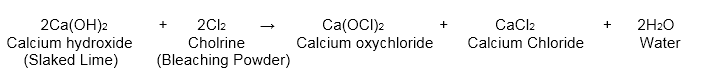
- It reacts with unsaturated hydrocarbons to give addition products and substitution products with saturated hydrocarbons.
Chlorine Poisoning
Chlorine is a chemical that counteracts bacterial development in stationary water. It’s utilized to purify sewage and commercial waste. It’s additionally an active ingredient in a few cleaning items.
Chlorine poisoning usually happens when you take in or breathe in the chemical. It reacts with water — incorporating the water in your digestive tract. it, thus, forms hydrochloric acid and hydrochlorous acid. Both of these substances are very harmful to our body.
You might be most acquainted with chlorine that is utilized as a part of pools. Be that as it may, most occurrences of chlorine poisoning come about because of ingesting household cleaners, not pool water. A couple of regular household items and substances containing chlorine include:
- Tablets utilized as a part of swimming pools
- Swimming pool water
- Mild household cleaners
- Bleaching products
Solved Example for You
Q: Mention some uses of chlorine.
Ans:
- We can use it as a bleaching agent. It is primarily used in the wood pulp, cotton and textile businesses.
- We use it regularly to clean drinking water. It is an antiseptic and disinfectant in swimming pools.
- It can be used in the extraction of gold and platinum. In the arrangement of harmful gasses, for example, phosgene, mustard gas and tear gas, we use chlorine.






Leave a Reply